Important note: this project is unfinished and unlikely to get finished any time soon. There are some strange bugs that cause the system to reset. Typing this out now makes me wonder if a smoothing capacitor would help...
This project set out to use an ESP32 microcontroller with a 3.2inch TFT ILI9341 touch screen to emulate a selection of different infrared remote controls.

Hardware
- The display is a 3.2 inch TFT ILI9341 resistive touch screen.
- The microcontroller is an ESP-WROOM-32 dev kit.
- The IR LED is a 5mm IR 940nm LED coupled with a 54ohm current limiting resistor.
As the IR Led has to use pin 4, the hookup is different to the original ILI9341 setup. None the less, the pinout is as follows:
- Anode of LED –> 54ohm resistor –> ESP32 GPIO 4
- Cathode of LED –> GND
- ILI9341 VCC –> ESP32 5V
- ILI9341 GND –> ESP32 GND
- ILI9341 CS –> ESP32 GPIO 15
- ILI9341 RST –> ESP32 GPIO 19
- ILI9341 D/C –> ESP32 GPIO 2
- ILI9341 SDI/MOSI –> ILI9341 T_DIN –> ESP32 GPIO 23
- ILI9341 SCK –> ILI9341 T_CLK –> ESP32 GPIO 18
- ILI9341 LED –> ESP32 5V (I’ve added a 330 ohm resistor in series for shits and giggles)
- ILI9341 SDO/MISO –> ILI9341 T_OUT –> ESP32 GPIO 19
- ILI9341 T_CS –> ESP32 GPIO 21
Preparation Setup
Part 1 – Preparing your images
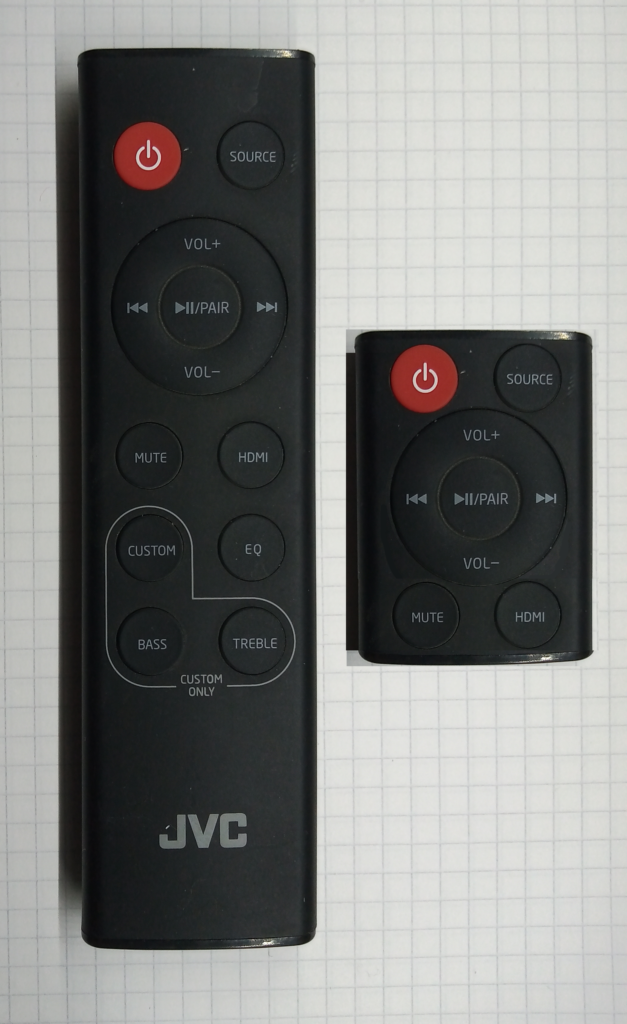
Firstly, photograph your remote controls in a good, flat light. I tried to scan the remote controls but the white balance and colours were all over the shop.
The display resolution of the display is 240×320 pixels. Therefore, you’ll need to digitally alter the photos to suit the aspect ratio. I found that removing the majority of the unused buttons can save a significant amount of space.
The image to the right shows the original photo on the left with the altered image on the right.
Once you have your images, you need to convert them to a .h file. I used this converter to produce a .c file, then resave as a .h.

Part 2: Obtain button data
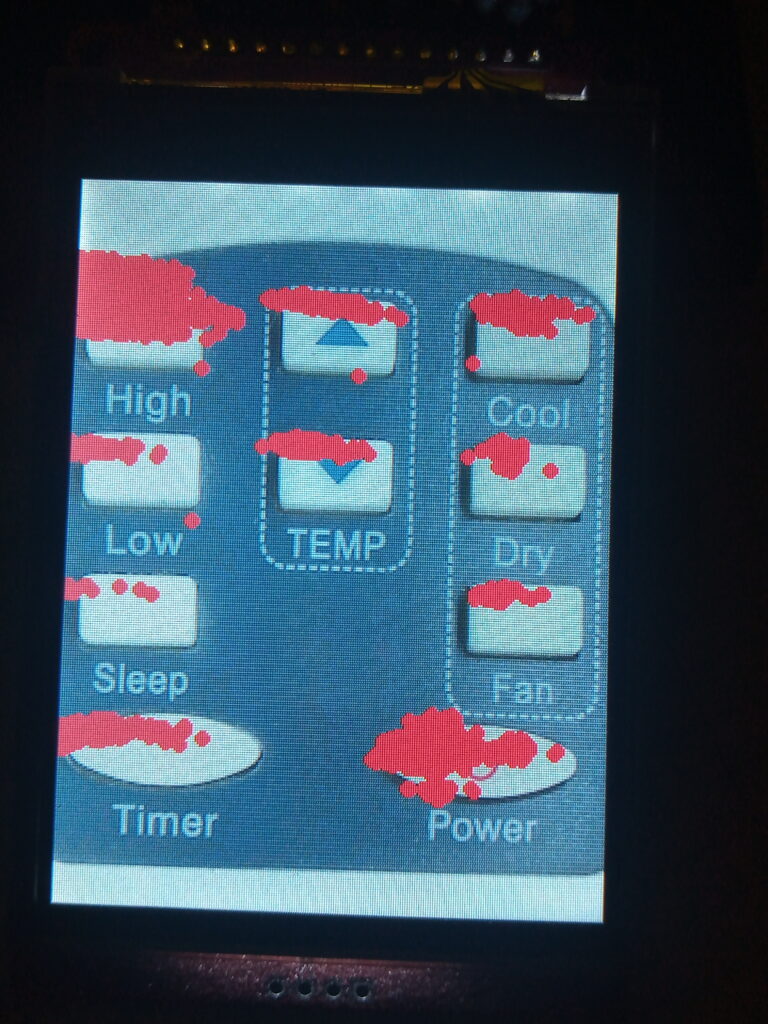
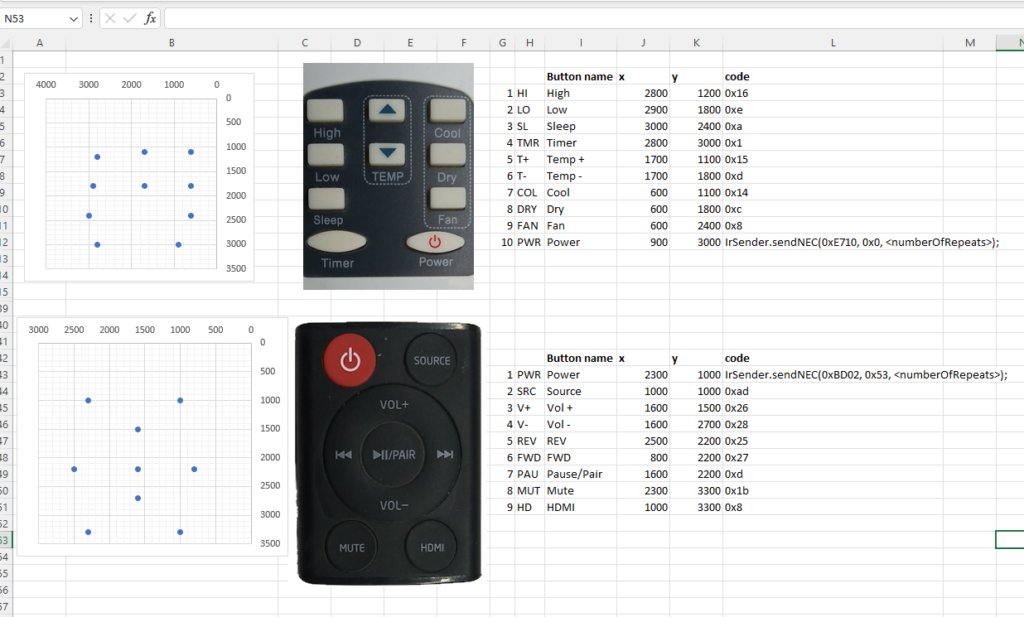
With this section, you have to upload the image to the display, tap the various buttons and record the x and y co-ordinate data.
To help in the process, I printed a red dot to a mapped location on the display.
All of the data is plotted to an excel chart (shown below), along with other useful information like the IR codes.
The graphs show the distribution of the button locations.
Software
User_Setup.h
As always, this example uses the TFT_eSPI library by Bodmer. And as such, you must set up the display in the User_Setup.h file. Below is the standard copy and paste of what I’ve used. Could I condense it down? Yes. Am I going to condense it down? No.
// USER DEFINED SETTINGS
// Set driver type, fonts to be loaded, pins used and SPI control method etc
//
// See the User_Setup_Select.h file if you wish to be able to define multiple
// setups and then easily select which setup file is used by the compiler.
//
// If this file is edited correctly then all the library example sketches should
// run without the need to make any more changes for a particular hardware setup!
// Note that some sketches are designed for a particular TFT pixel width/height
// User defined information reported by "Read_User_Setup" test & diagnostics example
#define USER_SETUP_INFO "User_Setup"
// Define to disable all #warnings in library (can be put in User_Setup_Select.h)
//#define DISABLE_ALL_LIBRARY_WARNINGS
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 1. Call up the right driver file and any options for it
//
// ##################################################################################
// Define STM32 to invoke optimised processor support (only for STM32)
//#define STM32
// Defining the STM32 board allows the library to optimise the performance
// for UNO compatible "MCUfriend" style shields
//#define NUCLEO_64_TFT
//#define NUCLEO_144_TFT
// STM32 8 bit parallel only:
// If STN32 Port A or B pins 0-7 are used for 8 bit parallel data bus bits 0-7
// then this will improve rendering performance by a factor of ~8x
//#define STM_PORTA_DATA_BUS
//#define STM_PORTB_DATA_BUS
// Tell the library to use parallel mode (otherwise SPI is assumed)
//#define TFT_PARALLEL_8_BIT
//#defined TFT_PARALLEL_16_BIT // **** 16 bit parallel ONLY for RP2040 processor ****
// Display type - only define if RPi display
//#define RPI_DISPLAY_TYPE // 20MHz maximum SPI
// Only define one driver, the other ones must be commented out
#define ILI9341_DRIVER // Generic driver for common displays
//#define ILI9341_2_DRIVER // Alternative ILI9341 driver, see https://github.com/Bodmer/TFT_eSPI/issues/1172
//#define ST7735_DRIVER // Define additional parameters below for this display
//#define ILI9163_DRIVER // Define additional parameters below for this display
//#define S6D02A1_DRIVER
//#define RPI_ILI9486_DRIVER // 20MHz maximum SPI
//#define HX8357D_DRIVER
//#define ILI9481_DRIVER
//#define ILI9486_DRIVER
//#define ILI9488_DRIVER // WARNING: Do not connect ILI9488 display SDO to MISO if other devices share the SPI bus (TFT SDO does NOT tristate when CS is high)
//#define ST7789_DRIVER // Full configuration option, define additional parameters below for this display
//#define ST7789_2_DRIVER // Minimal configuration option, define additional parameters below for this display
//#define R61581_DRIVER
//#define RM68140_DRIVER
//#define ST7796_DRIVER
//#define SSD1351_DRIVER
//#define SSD1963_480_DRIVER
//#define SSD1963_800_DRIVER
//#define SSD1963_800ALT_DRIVER
//#define ILI9225_DRIVER
//#define GC9A01_DRIVER
// Some displays support SPI reads via the MISO pin, other displays have a single
// bi-directional SDA pin and the library will try to read this via the MOSI line.
// To use the SDA line for reading data from the TFT uncomment the following line:
#define TFT_SDA_READ // This option is for ESP32 ONLY, tested with ST7789 and GC9A01 display only
// For ST7735, ST7789 and ILI9341 ONLY, define the colour order IF the blue and red are swapped on your display
// Try ONE option at a time to find the correct colour order for your display
// #define TFT_RGB_ORDER TFT_RGB // Colour order Red-Green-Blue
#define TFT_RGB_ORDER TFT_BGR // Colour order Blue-Green-Red
// For M5Stack ESP32 module with integrated ILI9341 display ONLY, remove // in line below
// #define M5STACK
// For ST7789, ST7735, ILI9163 and GC9A01 ONLY, define the pixel width and height in portrait orientation
// #define TFT_WIDTH 80
// #define TFT_WIDTH 128
// #define TFT_WIDTH 172 // ST7789 172 x 320
// #define TFT_WIDTH 240 // ST7789 240 x 240 and 240 x 320
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 160
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 128
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 240 // ST7789 240 x 240
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 320 // ST7789 240 x 320
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 240 // GC9A01 240 x 240
// For ST7735 ONLY, define the type of display, originally this was based on the
// colour of the tab on the screen protector film but this is not always true, so try
// out the different options below if the screen does not display graphics correctly,
// e.g. colours wrong, mirror images, or stray pixels at the edges.
// Comment out ALL BUT ONE of these options for a ST7735 display driver, save this
// this User_Setup file, then rebuild and upload the sketch to the board again:
// #define ST7735_INITB
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB2
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB3
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB128 // For 128 x 128 display
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB160x80 // For 160 x 80 display (BGR, inverted, 26 offset)
// #define ST7735_REDTAB
// #define ST7735_BLACKTAB
// #define ST7735_REDTAB160x80 // For 160 x 80 display with 24 pixel offset
// If colours are inverted (white shows as black) then uncomment one of the next
// 2 lines try both options, one of the options should correct the inversion.
// #define TFT_INVERSION_ON
// #define TFT_INVERSION_OFF
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 2. Define the pins that are used to interface with the display here
//
// ##################################################################################
// If a backlight control signal is available then define the TFT_BL pin in Section 2
// below. The backlight will be turned ON when tft.begin() is called, but the library
// needs to know if the LEDs are ON with the pin HIGH or LOW. If the LEDs are to be
// driven with a PWM signal or turned OFF/ON then this must be handled by the user
// sketch. e.g. with digitalWrite(TFT_BL, LOW);
// #define TFT_BL 32 // LED back-light control pin
// #define TFT_BACKLIGHT_ON HIGH // Level to turn ON back-light (HIGH or LOW)
// We must use hardware SPI, a minimum of 3 GPIO pins is needed.
// Typical setup for ESP8266 NodeMCU ESP-12 is :
//
// Display SDO/MISO to NodeMCU pin D6 (or leave disconnected if not reading TFT)
// Display LED to NodeMCU pin VIN (or 5V, see below)
// Display SCK to NodeMCU pin D5
// Display SDI/MOSI to NodeMCU pin D7
// Display DC (RS/AO)to NodeMCU pin D3
// Display RESET to NodeMCU pin D4 (or RST, see below)
// Display CS to NodeMCU pin D8 (or GND, see below)
// Display GND to NodeMCU pin GND (0V)
// Display VCC to NodeMCU 5V or 3.3V
//
// The TFT RESET pin can be connected to the NodeMCU RST pin or 3.3V to free up a control pin
//
// The DC (Data Command) pin may be labelled AO or RS (Register Select)
//
// With some displays such as the ILI9341 the TFT CS pin can be connected to GND if no more
// SPI devices (e.g. an SD Card) are connected, in this case comment out the #define TFT_CS
// line below so it is NOT defined. Other displays such at the ST7735 require the TFT CS pin
// to be toggled during setup, so in these cases the TFT_CS line must be defined and connected.
//
// The NodeMCU D0 pin can be used for RST
//
//
// Note: only some versions of the NodeMCU provide the USB 5V on the VIN pin
// If 5V is not available at a pin you can use 3.3V but backlight brightness
// will be lower.
// ###### EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE LINES FOLLOWING TO SUIT YOUR ESP8266 SETUP ######
// For NodeMCU - use pin numbers in the form PIN_Dx where Dx is the NodeMCU pin designation
//#define TFT_CS PIN_D8 // Chip select control pin D8
//#define TFT_DC PIN_D3 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to NodeMCU RST or 3.3V
//#define TFT_BL PIN_D1 // LED back-light (only for ST7789 with backlight control pin)
//#define TOUCH_CS PIN_D2 // Chip select pin (T_CS) of touch screen
//#define TFT_WR PIN_D2 // Write strobe for modified Raspberry Pi TFT only
// ###### FOR ESP8266 OVERLAP MODE EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE FOLLOWING LINES ######
// Overlap mode shares the ESP8266 FLASH SPI bus with the TFT so has a performance impact
// but saves pins for other functions. It is best not to connect MISO as some displays
// do not tristate that line when chip select is high!
// Note: Only one SPI device can share the FLASH SPI lines, so a SPI touch controller
// cannot be connected as well to the same SPI signals.
// On NodeMCU 1.0 SD0=MISO, SD1=MOSI, CLK=SCLK to connect to TFT in overlap mode
// On NodeMCU V3 S0 =MISO, S1 =MOSI, S2 =SCLK
// In ESP8266 overlap mode the following must be defined
//#define TFT_SPI_OVERLAP
// In ESP8266 overlap mode the TFT chip select MUST connect to pin D3
//#define TFT_CS PIN_D3
//#define TFT_DC PIN_D5 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to NodeMCU RST or 3.3V
// ###### EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE LINES FOLLOWING TO SUIT YOUR ESP32 SETUP ######
// For ESP32 Dev board (only tested with ILI9341 display)
// The hardware SPI can be mapped to any pins
#define TFT_MISO 19
#define TFT_MOSI 23 //changed TO this pin on 2023 01 06
#define TFT_SCLK 18 //changed TO this pin on 2023 01 06
#define TFT_CS 15 // Chip select control pin
#define TFT_DC 2 // Data Command control pin
#define TFT_RST 17 // Reset pin (could connect to RST pin)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if display RESET is connected to ESP32 board RST
// For ESP32 Dev board (only tested with GC9A01 display)
// The hardware SPI can be mapped to any pins
//#define TFT_MOSI 13 // In some display driver board, it might be written as "SDA" and so on.
//#define TFT_SCLK 14
//#define TFT_CS 5 // Chip select control pin
//#define TFT_DC 27 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST 33 // Reset pin (could connect to Arduino RESET pin)
//#define TFT_BL 22 // LED back-light
#define TOUCH_CS 21 // Chip select pin (T_CS) of touch screen
//#define TFT_WR 22 // Write strobe for modified Raspberry Pi TFT only
// For the M5Stack module use these #define lines
//#define TFT_MISO 19
//#define TFT_MOSI 23
//#define TFT_SCLK 18
//#define TFT_CS 14 // Chip select control pin
//#define TFT_DC 27 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST 33 // Reset pin (could connect to Arduino RESET pin)
//#define TFT_BL 32 // LED back-light (required for M5Stack)
// ###### EDIT THE PINs BELOW TO SUIT YOUR ESP32 PARALLEL TFT SETUP ######
// The library supports 8 bit parallel TFTs with the ESP32, the pin
// selection below is compatible with ESP32 boards in UNO format.
// Wemos D32 boards need to be modified, see diagram in Tools folder.
// Only ILI9481 and ILI9341 based displays have been tested!
// Parallel bus is only supported for the STM32 and ESP32
// Example below is for ESP32 Parallel interface with UNO displays
// Tell the library to use 8 bit parallel mode (otherwise SPI is assumed)
//#define TFT_PARALLEL_8_BIT
// The ESP32 and TFT the pins used for testing are:
//#define TFT_CS 33 // Chip select control pin (library pulls permanently low
//#define TFT_DC 15 // Data Command control pin - must use a pin in the range 0-31
//#define TFT_RST 32 // Reset pin, toggles on startup
//#define TFT_WR 4 // Write strobe control pin - must use a pin in the range 0-31
//#define TFT_RD 2 // Read strobe control pin
//#define TFT_D0 12 // Must use pins in the range 0-31 for the data bus
//#define TFT_D1 13 // so a single register write sets/clears all bits.
//#define TFT_D2 26 // Pins can be randomly assigned, this does not affect
//#define TFT_D3 25 // TFT screen update performance.
//#define TFT_D4 17
//#define TFT_D5 16
//#define TFT_D6 27
//#define TFT_D7 14
// ###### EDIT THE PINs BELOW TO SUIT YOUR STM32 SPI TFT SETUP ######
// The TFT can be connected to SPI port 1 or 2
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 1 // SPI port 1 maximum clock rate is 55MHz
//#define TFT_MOSI PA7
//#define TFT_MISO PA6
//#define TFT_SCLK PA5
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 2 // SPI port 2 maximum clock rate is 27MHz
//#define TFT_MOSI PB15
//#define TFT_MISO PB14
//#define TFT_SCLK PB13
// Can use Ardiuno pin references, arbitrary allocation, TFT_eSPI controls chip select
//#define TFT_CS D5 // Chip select control pin to TFT CS
//#define TFT_DC D6 // Data Command control pin to TFT DC (may be labelled RS = Register Select)
//#define TFT_RST D7 // Reset pin to TFT RST (or RESET)
// OR alternatively, we can use STM32 port reference names PXnn
//#define TFT_CS PE11 // Nucleo-F767ZI equivalent of D5
//#define TFT_DC PE9 // Nucleo-F767ZI equivalent of D6
//#define TFT_RST PF13 // Nucleo-F767ZI equivalent of D7
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to processor reset
// Use an Arduino pin for initial testing as connecting to processor reset
// may not work (pulse too short at power up?)
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 3. Define the fonts that are to be used here
//
// ##################################################################################
// Comment out the #defines below with // to stop that font being loaded
// The ESP8366 and ESP32 have plenty of memory so commenting out fonts is not
// normally necessary. If all fonts are loaded the extra FLASH space required is
// about 17Kbytes. To save FLASH space only enable the fonts you need!
#define LOAD_GLCD // Font 1. Original Adafruit 8 pixel font needs ~1820 bytes in FLASH
#define LOAD_FONT2 // Font 2. Small 16 pixel high font, needs ~3534 bytes in FLASH, 96 characters
#define LOAD_FONT4 // Font 4. Medium 26 pixel high font, needs ~5848 bytes in FLASH, 96 characters
#define LOAD_FONT6 // Font 6. Large 48 pixel font, needs ~2666 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.apm
#define LOAD_FONT7 // Font 7. 7 segment 48 pixel font, needs ~2438 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.
#define LOAD_FONT8 // Font 8. Large 75 pixel font needs ~3256 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.
//#define LOAD_FONT8N // Font 8. Alternative to Font 8 above, slightly narrower, so 3 digits fit a 160 pixel TFT
#define LOAD_GFXFF // FreeFonts. Include access to the 48 Adafruit_GFX free fonts FF1 to FF48 and custom fonts
// Comment out the #define below to stop the SPIFFS filing system and smooth font code being loaded
// this will save ~20kbytes of FLASH
#define SMOOTH_FONT
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 4. Other options
//
// ##################################################################################
// For RP2040 processor and SPI displays, uncomment the following line to use the PIO interface.
//#define RP2040_PIO_SPI // Leave commented out to use standard RP2040 SPI port interface
// For the RP2040 processor define the SPI port channel used (default 0 if undefined)
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 1 // Set to 0 if SPI0 pins are used, or 1 if spi1 pins used
// For the STM32 processor define the SPI port channel used (default 1 if undefined)
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 2 // Set to 1 for SPI port 1, or 2 for SPI port 2
// Define the SPI clock frequency, this affects the graphics rendering speed. Too
// fast and the TFT driver will not keep up and display corruption appears.
// With an ILI9341 display 40MHz works OK, 80MHz sometimes fails
// With a ST7735 display more than 27MHz may not work (spurious pixels and lines)
// With an ILI9163 display 27 MHz works OK.
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 1000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 5000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 10000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 20000000
#define SPI_FREQUENCY 27000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 40000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 55000000 // STM32 SPI1 only (SPI2 maximum is 27MHz)
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 80000000
// Optional reduced SPI frequency for reading TFT
#define SPI_READ_FREQUENCY 20000000
// The XPT2046 requires a lower SPI clock rate of 2.5MHz so we define that here:
#define SPI_TOUCH_FREQUENCY 2500000
// The ESP32 has 2 free SPI ports i.e. VSPI and HSPI, the VSPI is the default.
// If the VSPI port is in use and pins are not accessible (e.g. TTGO T-Beam)
// then uncomment the following line:
#define USE_HSPI_PORT
// Comment out the following #define if "SPI Transactions" do not need to be
// supported. When commented out the code size will be smaller and sketches will
// run slightly faster, so leave it commented out unless you need it!
// Transaction support is needed to work with SD library but not needed with TFT_SdFat
// Transaction support is required if other SPI devices are connected.
// Transactions are automatically enabled by the library for an ESP32 (to use HAL mutex)
// so changing it here has no effect
#define SUPPORT_TRANSACTIONS
Main Sketch
To be honest, there is no point copying and pasting the exact code used as it depends on what remote controls you want to use and how you want to use them. But in the spirit of good nature, I’ll go through the various sections of code.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <TFT_eSPI.h>
#include <IRremote.hpp>
#include "TVremote.h"
#include "ACremote.h"
#include "SBremote.h"
#define IR_SEND_PIN 4
TFT_eSPI tft = TFT_eSPI();
uint16_t x, y;
int averageX = 0;
int averageY = 0;
This is the inclusion of the various library and image header files.
The pin for the IR LED is also defined.
An instance of the display is created and some other variables are declared.
int buttonMapID = 1;
char AC_button[10][4] = {"HI", "LO", "SL", "TMR", "T+", "T-", "COL", "DRY", "FAN", "PWR"};
const int AC_code[10] = {0x16, 0xE, 0xA, 0x1, 0x15, 0xD, 0x14, 0xC, 0x8, 0x0};
const int AC_x[10] = {2800, 2900, 3000, 2800, 1700, 1700, 600, 600, 600, 900};
const int AC_y[10] = {1200, 1800, 2400, 3000, 1100, 1800, 1100, 1800, 2400, 3000};The buttonMapID is used with a switch:case statement later to filter which ‘map’ to use.
The declaration includes a set of an array of character arrays for the button names for debugging and testing purposes.
The codes, x and y co-ordinates are also saved as an array. These are the figures obtained through the previous testing.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
IrSender.begin(IR_SEND_PIN);
tft.init();
tft.setSwapBytes(true);
tft.setRotation(2);
tft.fillScreen(TFT_BLACK);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, TFT_BLACK);
tft.drawString("Loading Touchscreen IR Remote...", 10, 10, 2);
delay(1000);
remoteMenu();
}The setup function does what the setup function says it does and sets up the display, Serial communication and then sends the user to the ominous remoteMenu() function. More on that later.
void loop() {
if (tft.getTouchRawZ() > 600) {
getAverageReading(1);
printPixel();
if (y < 800) {
delay(100);
remoteMenu();
Serial.println("REMOTE MENU");
} else {
delay(100);
findClosestButton(x, y, buttonMapID);
}
}
}The loop is simple; it detects if there is a touch, obtains the x and y co-ordinates with the getAverageReading(x) function.
If the Y value is at the top of the screen then it sends the user to the ominous remoteMenu() function.
Else it will obtain the closest button match with the aptly named findClosestButton() function.
void getAverageReading(int readings) {
for (int i = 0; i < readings; i++) {
tft.getTouchRaw(&x, &y);
Serial.print("X value: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", Y value: ");
Serial.println(y);
delay(25);
}
}I’ll be honest. This is a vestigial function which has fallen by the wayside.
It used to accept an integer for the number of readings and return a mean average, but didn’t work that well and I’ve not got around to binning it completely.
void printPixel() {
int mapX = map(x, 2800, 300, 10, 220);
int mapY = map(y, 750, 3600, 10, 300);
tft.fillCircle(mapX, mapY, 3, TFT_RED);
}Prints a red dot where a touch is detected. This mapping is crude at best.
void findClosestButton(int _x, int _y, int _id) {
Serial.print("Button Map ID = "); Serial.println(_id);
switch (_id) {
case 1: //TV
Serial.println("TV");
for (int xc = 0; xc < 20; xc++) {
int abs_diff_x = abs(x - TV_x[xc]);
if (abs_diff_x < 200) {
int abs_diff_y = abs(y - TV_y[xc]);
if (abs_diff_y < 200) {
Serial.println(TV_button[xc]);
IrSender.sendNEC(0xBF00, TV_code[xc], 3);
break;
}
}
}
break;
case 2: //AC
Serial.println("AC");
for (int xc = 0; xc < 20; xc++) {
int abs_diff_x = abs(x - AC_x[xc]);
if (abs_diff_x < 200) {
int abs_diff_y = abs(y - AC_y[xc]);
if (abs_diff_y < 200) {
Serial.println(AC_button[xc]);
IrSender.sendNEC(0xE710, AC_code[xc], 3);
break;
}
}
}
break;
case 3: //SB
Serial.println("SB");
for (int xc = 0; xc < 20; xc++) {
int abs_diff_x = abs(x - SB_x[xc]);
if (abs_diff_x < 200) {
int abs_diff_y = abs(y - SB_y[xc]);
if (abs_diff_y < 200) {
Serial.println(SB_button[xc]);
break;
}
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
delay(100);
}This is the meat and potatoes of the sketch, but also fairly simple.
The for loop goes through and finds the absolute difference between the x-coordinate values of the remote buttons and that detected in the touch. If that difference is within a nominal distance then it checks to see if the y-coordinate is within the same nominal distance.
void remoteMenu() {
tft.fillScreen(TFT_BLACK);
tft.drawString("HJWWALTERS.COM", 3, 0, 4);
for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) {
int mly = 20 + (100 * l);
tft.drawLine(0, mly, 240, mly, TFT_WHITE);
}
tft.drawString("TV", 80, 50, 4);
tft.drawString("AC", 80, 150, 4);
tft.drawString("Sound Bar", 60, 250, 4);
while (tft.getTouchRawZ() < 600);
tft.getTouchRaw(&x, &y);
buttonMapID = y / 1000;
switch (buttonMapID) {
case 1: //TV
tft.pushImage(0, 0, 240, 320, TVremote);
break;
case 2: //AC
tft.pushImage(0, 0, 240, 320, ACremote);
break;
case 3: //SB
tft.pushImage(0, 0, 240, 320, SBremote);
break;
default:
break;
}
delay(100);
}This is the ominous “remoteMenu” function. Basically draws the menu page.
The button map ID is a bit of a hack, as I noticed that the top button had typical y-coordinate values of 1000-1900, the second button for values around 2000-2900,… etc, so the raw value is divided by 1000 to truncate it to the first digit.
Final Comments
This was only ever going to be a quick weekend project and after finding numerous difficult bugs, I’ve decided to box it up. I think a capacitive touch screen would be much better for this purpose as it would be more accurate.
Page created: 18/08/2024
Last updated: 18/08/2024